What does PDA mean? Why does the ductus arteriosus close off at the time of birth? Patent ductus arteriosus ( PDA ) is treated with medicines, catheter-based procedures, and surgery. The goal of treatment is to close the PDA to prevent complications and reverse the effects of increased blood volume. Small PDAs often close without treatment.
The procedure may be performed as Open surgery : the surgeon accesses the thoracic cavity through a large incision in the chest (thoracotomy) and uses standard surgical instruments to perform the procedure. Naturally, immediately after birth, the ductus arteriosus is supposed to close so that oxygenated blood can be supplied by lungs through the air. In a few cases, the ductus arteriosus fails to close (or patent), leaving an open hole in the heart.
This is referred to as Patent Ductus Arteriosus (PDA). A chil at any age, can have surgery to close the patent ductus arteriosus. Surgery is the best option for a child who have a very large patent ductus arteriosus or other unusual anatomy.
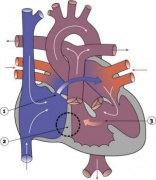
If your child has surgery : A small incision is made between the ribs on the left side. In the womb, the mother’s placenta provides oxygen for the baby and the ductus arteriosus allows blood to bypass the lungs. After birth, the baby must use their lungs to take in oxygen and get rid of carbon dioxide. To achieve this, the blood flows to the lungs and the ductus arteriosus closes. The ductus arteriosus is there to bypass the lungs.
Instea it sends blood straight from the pulmonary arteries to the aorta. If it doesn’t close, blood can flow backward from the aorta to the. It’s an extra blood vessel that connects arteries: the pulmonary artery and the aorta.
The pulmonary artery carries blood from the heart to the lungs. PDA ( Patent Ductus Arteriosus ) ligation is a surgical operation for children whose ductus arteriosus did not close after birth. The Ductus Arteriosus is a connection between the main blood vessel to the body (the Aorta) and the main blood vessel to the Lungs (Pulmonary Artery) which is needed in babies before they are born, but usually closes on its own some time in the first. Actually, every human being is born with one. But in most of us, it closes in the first day or two of life as the newborn takes its first breaths.
Cardiopulmonary bypass with balloon occlusion provides a safe operation for adult patients with complicated patent ductus arteriosus. The majority of patent ductus arteriosus (PDA) patients undergo a surgical correction in childhood. However, some situations retard the operation until adulthood.
PDA is a heart problem that is usually noted in the first few weeks or months after birth. All babies are born with this opening between the aorta and the pulmonary artery. But it usually closes on its own shortly after birth. If it stays open, it is called patent ductus arteriosus. In summary, the thoracoscopic PDA closure should be performed only in the selected centers with VATS and surgical closure experience to minimize the effect of the learning curve.
PDA, patent ductus arteriosus. The development of transcatheter devices allows to operate even on preterm infants with extremely low birth weight. When this happens, it allows some of the baby’s blood to bypass the lungs. This is usually carried out within a few weeks of birth.
The abnormal blood vessel will be split to create new blood vessels, and each one will be reconnected in the correct position. As part of the fetal circulation, the ductus arteriosus allows the majority of circulating blood to bypass the lungs. Therefore, while the fetus is in the uterus, the ductus arteriosus is normally open, or “patent.
When the newborn puppy takes its first breath, the ductus is stimulated to close down.
No comments:
Post a Comment
Note: only a member of this blog may post a comment.